How to Understand Your Property's Plumbing System Anatomy
How to Understand Your Property's Plumbing System Anatomy
Blog Article
Listed here further down you can locate a bunch of decent information and facts in regards to Exploring Your Homes Plumbing Anatomy.
Recognizing just how your home's plumbing system works is vital for each house owner. From providing clean water for drinking, cooking, and bathing to safely getting rid of wastewater, a properly maintained pipes system is critical for your family members's wellness and convenience. In this detailed guide, we'll discover the elaborate network that makes up your home's plumbing and deal pointers on upkeep, upgrades, and managing usual concerns.
Intro
Your home's plumbing system is more than simply a network of pipelines; it's a complicated system that ensures you have access to tidy water and reliable wastewater removal. Recognizing its parts and exactly how they interact can help you prevent costly repairs and ensure everything runs smoothly.
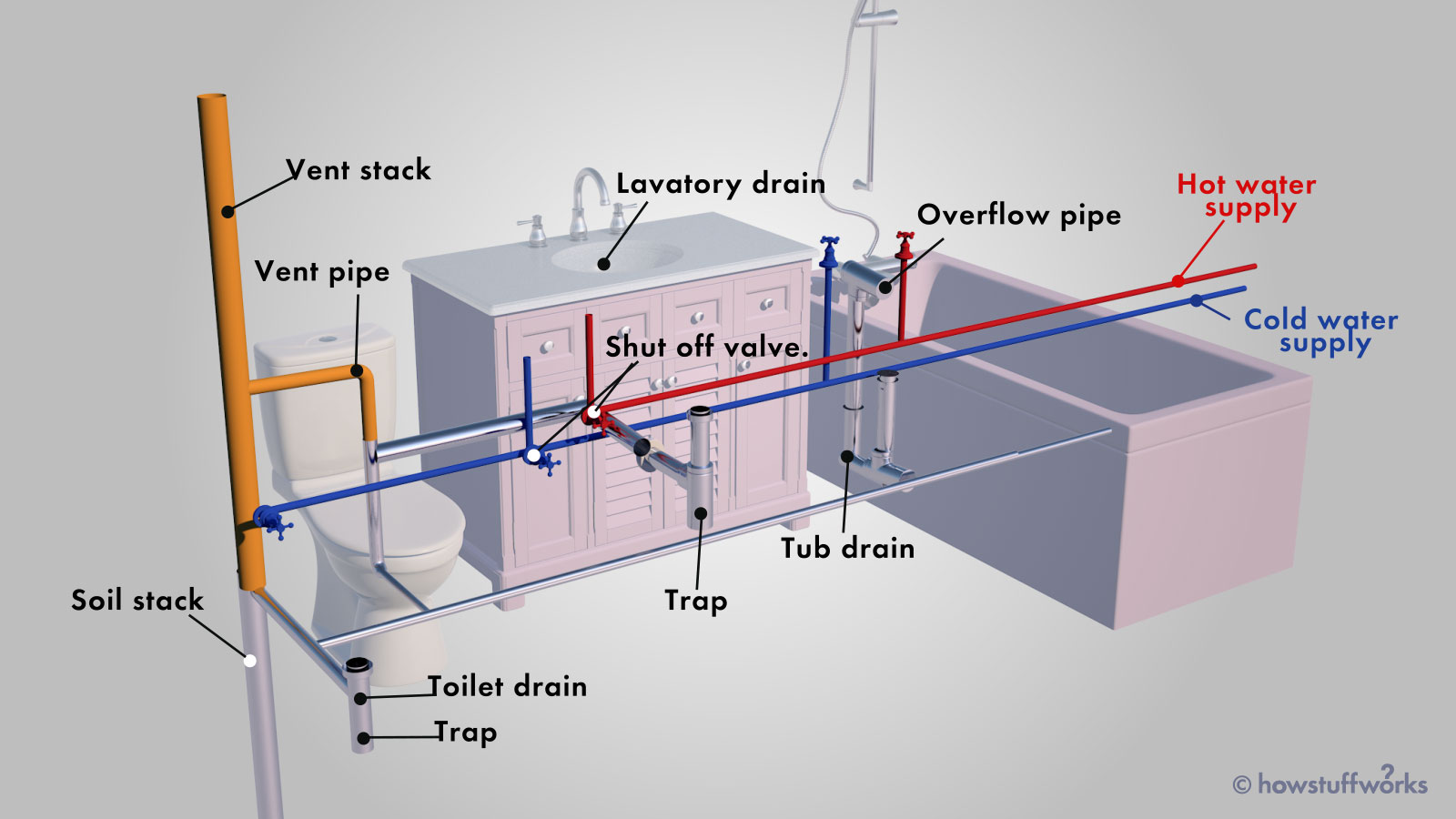
Basic Components of a Pipes System
Pipelines and Tubing
At the heart of your plumbing system are the pipes and tubing that lug water throughout your home. These can be made from numerous materials such as copper, PVC, or PEX, each with its advantages in regards to toughness and cost-effectiveness.
Components: Sinks, Toilets, Showers, and so on.
Fixtures like sinks, commodes, showers, and tubs are where water is used in your house. Comprehending how these fixtures connect to the pipes system helps in detecting problems and preparing upgrades.
Shutoffs and Shut-off Points
Valves regulate the flow of water in your pipes system. Shut-off shutoffs are crucial throughout emergencies or when you need to make fixings, allowing you to separate parts of the system without disrupting water circulation to the whole residence.
Water System System
Key Water Line
The primary water line links your home to the community water supply or an exclusive well. It's where water enters your home and is dispersed to numerous components.
Water Meter and Stress Regulator
The water meter measures your water use, while a stress regulator guarantees that water flows at a secure pressure throughout your home's plumbing system, stopping damages to pipelines and fixtures.
Cold Water vs. Hot Water Lines
Comprehending the difference between cold water lines, which provide water straight from the main, and warm water lines, which lug warmed water from the water heater, assists in repairing and planning for upgrades.
Drain System
Drain Water Lines and Traps
Drain pipelines carry wastewater far from sinks, showers, and commodes to the sewage system or sewage-disposal tank. Traps prevent drain gases from entering your home and likewise trap particles that could trigger blockages.
Ventilation Pipes
Air flow pipelines permit air into the drain system, stopping suction that can reduce water drainage and create catches to empty. Proper ventilation is necessary for preserving the stability of your pipes system.
Relevance of Correct Water Drainage
Ensuring correct water drainage protects against backups and water damages. Routinely cleaning drains and maintaining traps can prevent expensive repair work and extend the life of your plumbing system.
Water Heating Unit
Types of Water Heaters
Hot water heater can be tankless or typical tank-style. Tankless heating units warm water on demand, while tanks store heated water for prompt usage.
Just How Water Heaters Attach to the Pipes System
Recognizing just how hot water heater link to both the cold water supply and hot water distribution lines aids in identifying issues like insufficient warm water or leaks.
Maintenance Tips for Water Heaters
Regularly purging your hot water heater to remove sediment, checking the temperature level settings, and evaluating for leakages can extend its life-span and boost energy performance.
Typical Pipes Problems
Leaks and Their Reasons
Leaks can happen because of maturing pipes, loose installations, or high water pressure. Dealing with leakages quickly stops water damages and mold and mildew development.
Obstructions and Clogs
Obstructions in drains pipes and commodes are usually brought on by flushing non-flushable products or an accumulation of oil and hair. Utilizing drain screens and bearing in mind what goes down your drains can protect against obstructions.
Indications of Plumbing Troubles to Expect
Low water stress, sluggish drains, foul odors, or unusually high water costs are indications of prospective plumbing issues that need to be resolved quickly.
Plumbing Maintenance Tips
Normal Examinations and Checks
Arrange annual pipes assessments to capture problems early. Search for signs of leakages, deterioration, or mineral accumulation in faucets and showerheads.
DIY Upkeep Tasks
Straightforward jobs like cleaning tap aerators, checking for commode leaks making use of dye tablet computers, or insulating revealed pipes in cool climates can stop significant pipes problems.
When to Call an Expert Plumbing
Know when a pipes concern requires expert proficiency. Trying complex repair work without correct understanding can bring about more damages and higher repair service costs.
Upgrading Your Pipes System
Reasons for Updating
Updating to water-efficient fixtures or replacing old pipelines can boost water quality, decrease water expenses, and raise the value of your home.
Modern Pipes Technologies and Their Benefits
Check out technologies like wise leak detectors, water-saving bathrooms, and energy-efficient water heaters that can conserve cash and decrease ecological impact.
Expense Considerations and ROI
Determine the upfront prices versus long-term financial savings when thinking about pipes upgrades. Numerous upgrades spend for themselves through lowered energy bills and less repair services.
Ecological Impact and Preservation
Water-Saving Fixtures and Home Appliances
Mounting low-flow faucets, showerheads, and commodes can considerably lower water usage without compromising performance.
Tips for Reducing Water Use
Easy behaviors like repairing leaks immediately, taking much shorter showers, and running complete tons of laundry and meals can conserve water and lower your energy bills.
Eco-Friendly Pipes Options
Think about lasting pipes materials like bamboo for flooring, which is durable and eco-friendly, or recycled glass for counter tops.
Emergency situation Readiness
Steps to Take Throughout a Pipes Emergency
Know where your shut-off valves lie and just how to shut off the supply of water in case of a ruptured pipe or significant leak.
Value of Having Emergency Contacts Convenient
Maintain get in touch with information for neighborhood plumbing technicians or emergency solutions easily available for quick response throughout a pipes dilemma.
Do It Yourself Emergency Situation Fixes (When Appropriate).
Short-lived solutions like using air duct tape to spot a leaking pipeline or putting a container under a leaking faucet can reduce damage up until an expert plumbing technician shows up.
Conclusion.
Understanding the anatomy of your home's plumbing system equips you to preserve it efficiently, saving time and money on repairs. By adhering to normal upkeep routines and staying notified regarding contemporary pipes modern technologies, you can guarantee your pipes system runs effectively for many years ahead.
Anatomy of a House: Understanding the Components of your Home (Part 2/3)
Windows/Doors
Windows are pretty simple. They will lean into the frame of your house and have trim/caulk added on both sides of the wall for aesthetics and protection from rain. As of today, the building standard is a vinyl, double hung window. If you look at any window in your house, you ll probably see two main sections of glass, one top section and one bottom section. Those are each called a sash. If they can both move and slide up and down, you have a double hung. Most newer, vinyl windows also have two glass panes in each sash with gas between them for energy efficiency.
The oldest type of window you would see on a typical basis would be the wooden window (everything but the glass is wood). Not long after, metal and aluminum windows became typical. It was perhaps around the early 2000s that vinyl started to become the growing standard. The most typical advantages to updated windows would be a lower energy bill, aesthetics, and function (old windows may stick or have cracked panes, etc).
Moving past the basics, the main pro tip we have is to keep an eye on windows for a subtle leak around the outside allowing rainwater past the siding. This will rot out and damage the frame of your house and wherever else the water gets to. Windows should have a nice caulked-in seal around the outside after the trim is wrapped around the window. If the drywall looks unusual under the window, this could be a sign of water getting in.
Doors are even more simple! However, there is common problem with exterior doors that doesn t seem to go away. When doors don t have an awning or at least an eve extended a little past the exterior wall, it is inevitable that the bottom outside wood of the door frame will rot. There are some door trim materials that are resistant to water damage, but time is not in their favor. All exterior doors are best to have some sort of rain cover.
Plumbing
Plumbing is known for being sneaky! Hidden in the walls and floor joists, it s hard to know there s a problem until visible damage has been done.
There are two systems in your plumbing: supply and drain.
Supply Lines
Supply plumbing comes from the city. In Davidson County of Tennessee, most water meters are in the ground of the front yard near the street. This is your main water valve and each 90 degrees of rotation on the valve will alternate between on and off. The primary differential of supply plumbing is that it is pressurized to push water out of your faucets. Thus, the pipe materials used must be strong and a sprung leak would mean a lot of damage to surrounding parts of the house very quickly. The supply plumbing also has two systems: hot and cold. Some of the water from the main line goes straight to your water heater, and is then pushed out to all the hot sides of the fixtures.
Supply pipe material has evolved. Starting around the 1960s, Galvanized pipe was perhaps the original standard but is cause for concern if seen in a house today. Eventually copper became the preferred material and is still considered up to code and acceptable. In recent years, PEX has gained market share for it s flexibility (easy to install, harder to break) while still maintaining the strength to hold the water pressure. Most homes built today will use PEX throughout. The commonly-toted advantage of PEX piping is its ability to expand if the water inside were to ever freeze, thus preventing a leak.
Plumbing fixture is an important term to know as it refers to anywhere the supply pipe converts to a valve to be controlled by a person for their use. Faucets, shower handles, outside spigots are all fixtures.
Drain Lines
Drain, also known as sewer, pipes deliver drain and toilet contents back to the city for water treatment. They were built cast iron or even lead for many years. Both can last perhaps 100 years, but if any are seen in a house today, they are likely due to be replaced at any moment. The standard for drain pipes for several decades has been the white PVC pipe (pictured here).
Drain lines aren t pressurized, so a leak wouldn t be nearly as catastrophic. A little bit of maintenance and care goes a long way with these lines as most damage we ve seen was easily preventable if the homeowner or tenants had paid attention. Common problem areas are under the toilet where bowl contents drop into the pipe and where the corners of the floor meet the bathtub/shower and wall (floor will be spongy ). Drain lines also have the bonus feature of being able to clog! Be careful of what you send down the drain or toilet, as a child s toy could become a $1000 repair!
To sum the plumbing section, a homeowner should take care in simply paying attention to symptoms of problems, and repairing right away. The longer a plumbing issue can carry on, the further the extent of damage. In a single story home, plumbing is almost always run between joists under the floors. They will take the shortest route from the main line outside, straight to the faucets or water heater. Drain lines will maintain a constant slope under the house until, typically, they converge into one big pipe that runs back to the city.
Electrical
The electrical system in your house is mostly known for the incredible conveniences it allows as well as for it s capacity for danger. Power runs from the the utility company into the Breaker Box AKA Electrical Panel. This panel splits the power into separate circuits and sends them out to various areas of the house. The circuits will have mostly outlets emerging from the walls, the circuits will also run power straight to some fixtures such as lights or a water heater.
*When it comes to safety, the most important fact to remember is that your body has to be the path that completes a circuit for electricity to flow through you and shock or electrocute you. This law manifests itself in many different ways.*
Much like all the other systems of the house, electrical has continued to innovate over the decades. The two big changes are breaker panels and grounded wires. Electrical Panels are now constructed with breakers. If something shorts, it trips a breaker instead of blowing a fuse. If your outlets only have two holes, your system is not grounded. Grounded circuits are safer and two-prong outlets are cause for concern. Another of the latest upgrades is a new type of outlet called GFCI that provides additional protection for outlets near water sources (typically kitchen and bath).
Electrical problems can be hard to predict and take many shapes and forms. The good thing is, however, most homeowners
https://skylinehomesolutions.com/anatomy-house-understanding-components-home-part-2-3/

Anatomy of a House: Understanding the Components of your Home (Part 2/3)
Windows/Doors
Windows are pretty simple. They will lean into the frame of your house and have trim/caulk added on both sides of the wall for aesthetics and protection from rain. As of today, the building standard is a vinyl, double hung window. If you look at any window in your house, you ll probably see two main sections of glass, one top section and one bottom section. Those are each called a sash. If they can both move and slide up and down, you have a double hung. Most newer, vinyl windows also have two glass panes in each sash with gas between them for energy efficiency.
The oldest type of window you would see on a typical basis would be the wooden window (everything but the glass is wood). Not long after, metal and aluminum windows became typical. It was perhaps around the early 2000s that vinyl started to become the growing standard. The most typical advantages to updated windows would be a lower energy bill, aesthetics, and function (old windows may stick or have cracked panes, etc).
Moving past the basics, the main pro tip we have is to keep an eye on windows for a subtle leak around the outside allowing rainwater past the siding. This will rot out and damage the frame of your house and wherever else the water gets to. Windows should have a nice caulked-in seal around the outside after the trim is wrapped around the window. If the drywall looks unusual under the window, this could be a sign of water getting in.
Doors are even more simple! However, there is common problem with exterior doors that doesn t seem to go away. When doors don t have an awning or at least an eve extended a little past the exterior wall, it is inevitable that the bottom outside wood of the door frame will rot. There are some door trim materials that are resistant to water damage, but time is not in their favor. All exterior doors are best to have some sort of rain cover.
Plumbing
Plumbing is known for being sneaky! Hidden in the walls and floor joists, it s hard to know there s a problem until visible damage has been done.
There are two systems in your plumbing: supply and drain.
Supply Lines
Supply plumbing comes from the city. In Davidson County of Tennessee, most water meters are in the ground of the front yard near the street. This is your main water valve and each 90 degrees of rotation on the valve will alternate between on and off. The primary differential of supply plumbing is that it is pressurized to push water out of your faucets. Thus, the pipe materials used must be strong and a sprung leak would mean a lot of damage to surrounding parts of the house very quickly. The supply plumbing also has two systems: hot and cold. Some of the water from the main line goes straight to your water heater, and is then pushed out to all the hot sides of the fixtures.
Supply pipe material has evolved. Starting around the 1960s, Galvanized pipe was perhaps the original standard but is cause for concern if seen in a house today. Eventually copper became the preferred material and is still considered up to code and acceptable. In recent years, PEX has gained market share for it s flexibility (easy to install, harder to break) while still maintaining the strength to hold the water pressure. Most homes built today will use PEX throughout. The commonly-toted advantage of PEX piping is its ability to expand if the water inside were to ever freeze, thus preventing a leak.
Plumbing fixture is an important term to know as it refers to anywhere the supply pipe converts to a valve to be controlled by a person for their use. Faucets, shower handles, outside spigots are all fixtures.
Drain Lines
Drain, also known as sewer, pipes deliver drain and toilet contents back to the city for water treatment. They were built cast iron or even lead for many years. Both can last perhaps 100 years, but if any are seen in a house today, they are likely due to be replaced at any moment. The standard for drain pipes for several decades has been the white PVC pipe (pictured here).
Drain lines aren t pressurized, so a leak wouldn t be nearly as catastrophic. A little bit of maintenance and care goes a long way with these lines as most damage we ve seen was easily preventable if the homeowner or tenants had paid attention. Common problem areas are under the toilet where bowl contents drop into the pipe and where the corners of the floor meet the bathtub/shower and wall (floor will be spongy ). Drain lines also have the bonus feature of being able to clog! Be careful of what you send down the drain or toilet, as a child s toy could become a $1000 repair!
To sum the plumbing section, a homeowner should take care in simply paying attention to symptoms of problems, and repairing right away. The longer a plumbing issue can carry on, the further the extent of damage. In a single story home, plumbing is almost always run between joists under the floors. They will take the shortest route from the main line outside, straight to the faucets or water heater. Drain lines will maintain a constant slope under the house until, typically, they converge into one big pipe that runs back to the city.
Electrical
The electrical system in your house is mostly known for the incredible conveniences it allows as well as for it s capacity for danger. Power runs from the the utility company into the Breaker Box AKA Electrical Panel. This panel splits the power into separate circuits and sends them out to various areas of the house. The circuits will have mostly outlets emerging from the walls, the circuits will also run power straight to some fixtures such as lights or a water heater.
*When it comes to safety, the most important fact to remember is that your body has to be the path that completes a circuit for electricity to flow through you and shock or electrocute you. This law manifests itself in many different ways.*
Much like all the other systems of the house, electrical has continued to innovate over the decades. The two big changes are breaker panels and grounded wires. Electrical Panels are now constructed with breakers. If something shorts, it trips a breaker instead of blowing a fuse. If your outlets only have two holes, your system is not grounded. Grounded circuits are safer and two-prong outlets are cause for concern. Another of the latest upgrades is a new type of outlet called GFCI that provides additional protection for outlets near water sources (typically kitchen and bath).
Electrical problems can be hard to predict and take many shapes and forms. The good thing is, however, most homeowners
https://skylinehomesolutions.com/anatomy-house-understanding-components-home-part-2-3/
Do you really like more info about The Inner Workings of Your Home's Plumbing? Make feedback directly below. We'd be glad to listen to your thinking about this write-up. Hoping to see you back again soon. In case you liked our post if you please consider to pass it around. Thank-you for your time spent reading it.
Start Now Report this page